Firstly, we strongly advise you to visually check the crankshaft sensor; i.e., its connector (poor connection or loosening of the connector), and its wiring (presence of damaged wires).
Secondly, you can test your sensor’s correct functioning by checking its resistance. However, the tests to be conducted will depend on the technology of the sensor.
For an inductive sensor (VRS), you will need to check the resistance with a multimeter – it should be between 300 and 900 Ω, depending on the manufacturer. You can also check the continuity of the electrical wires linking the sensor to the ECU (=0 Ω).
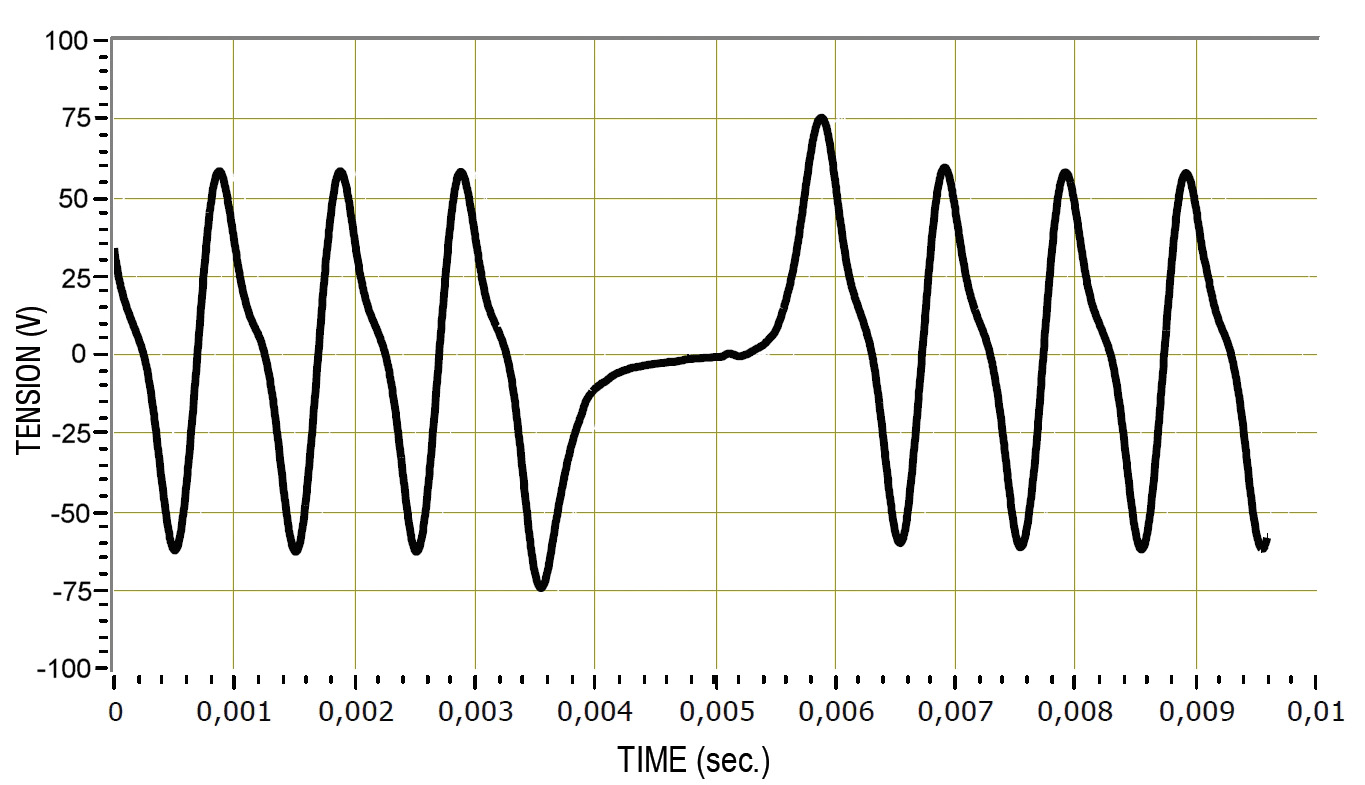
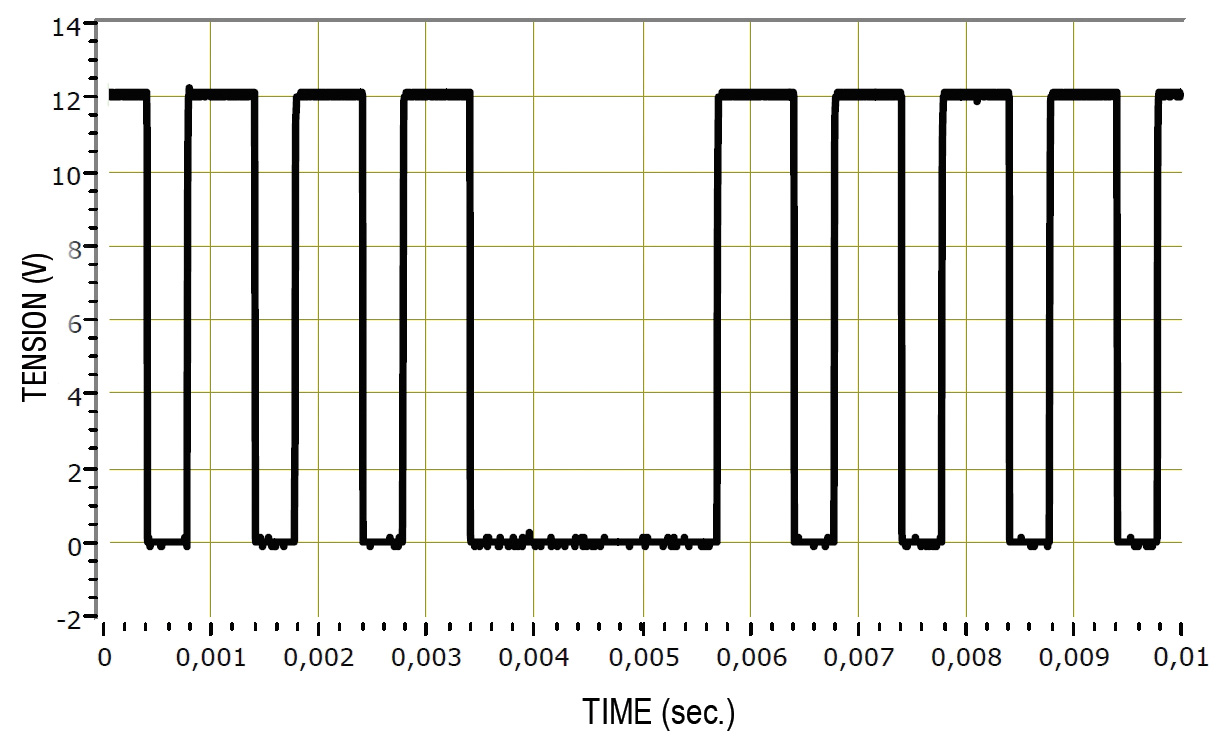
For a Hall Effect sensor, you will need an oscilloscope to measure the electrical signal. Make sure you have disconnected the ECU side connector and then check that there is a signal present by starting the engine.
If the above tests are not conclusive, then it would appear that you need to replace your vehicle’s crankshaft sensor.