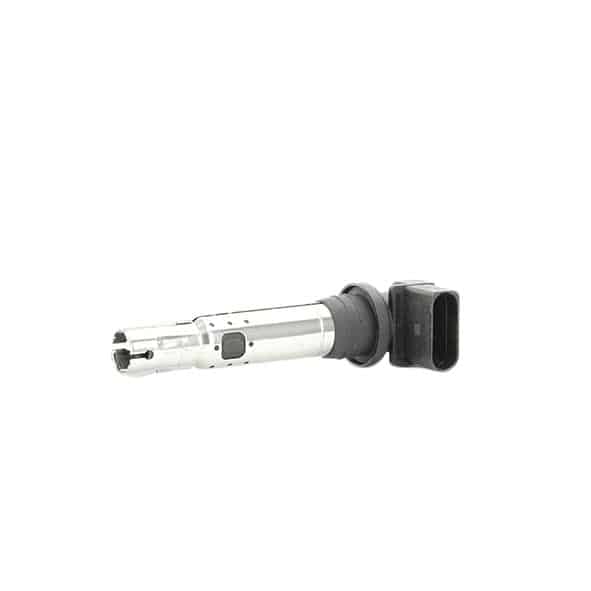
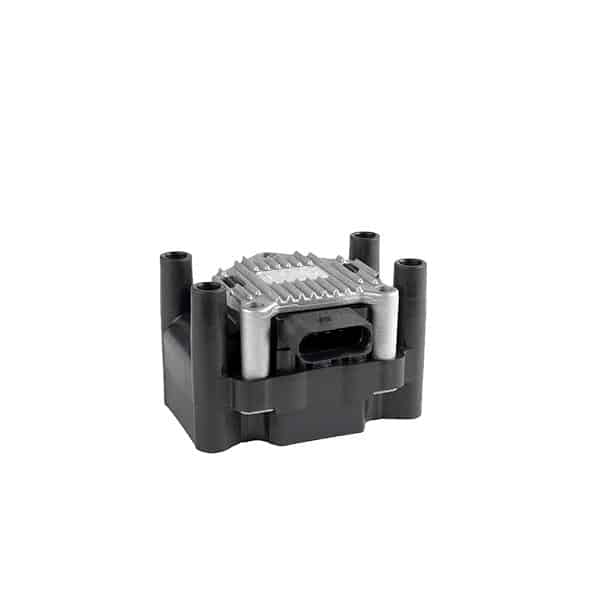
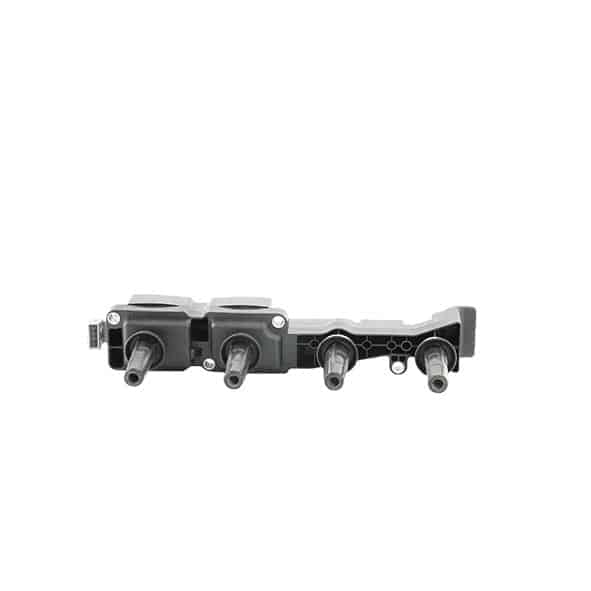
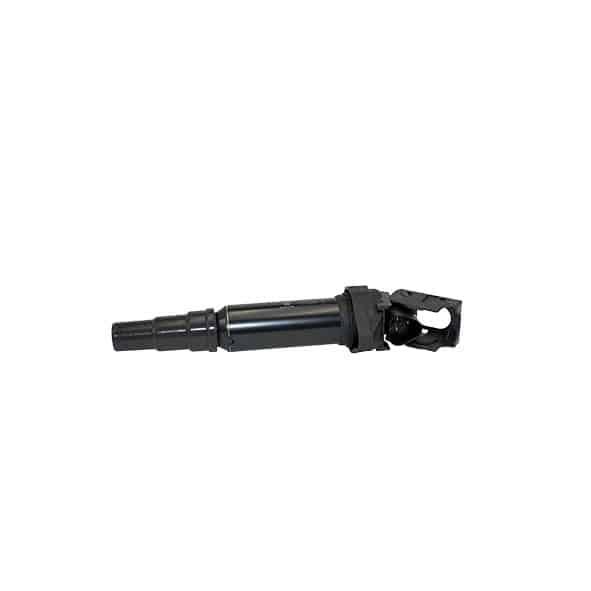
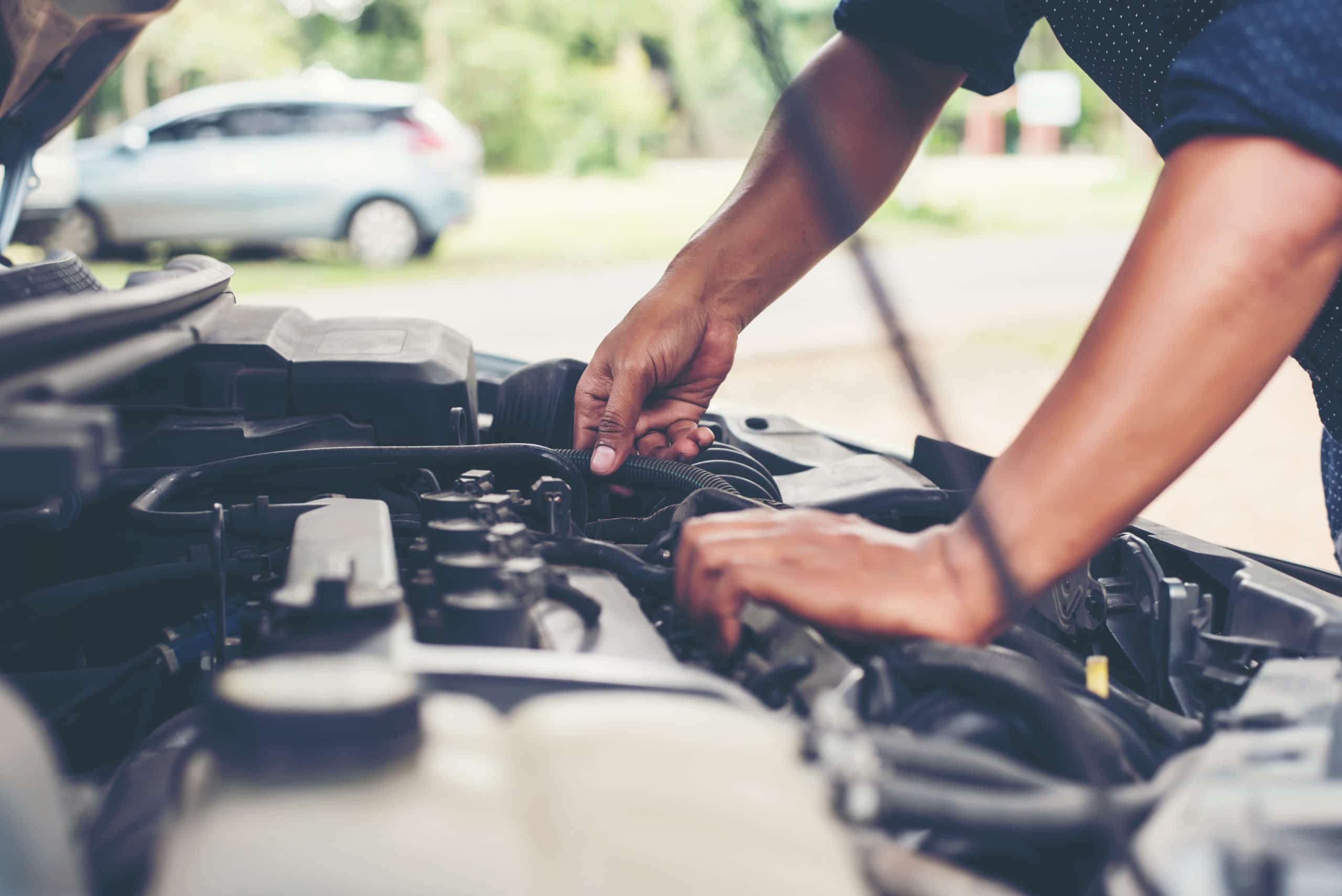
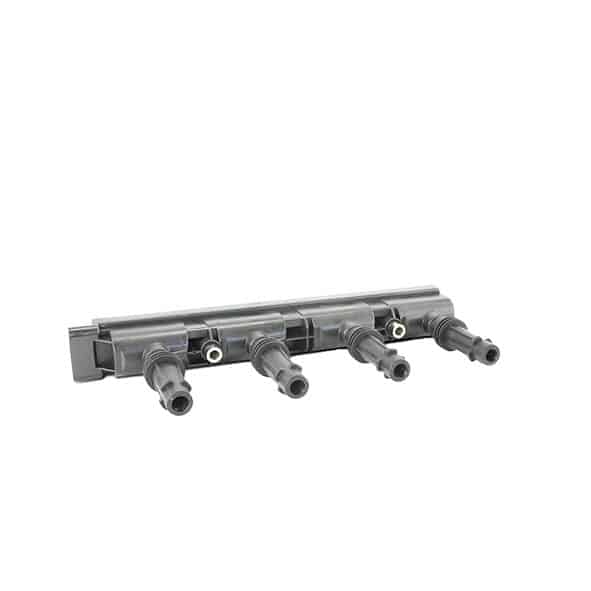
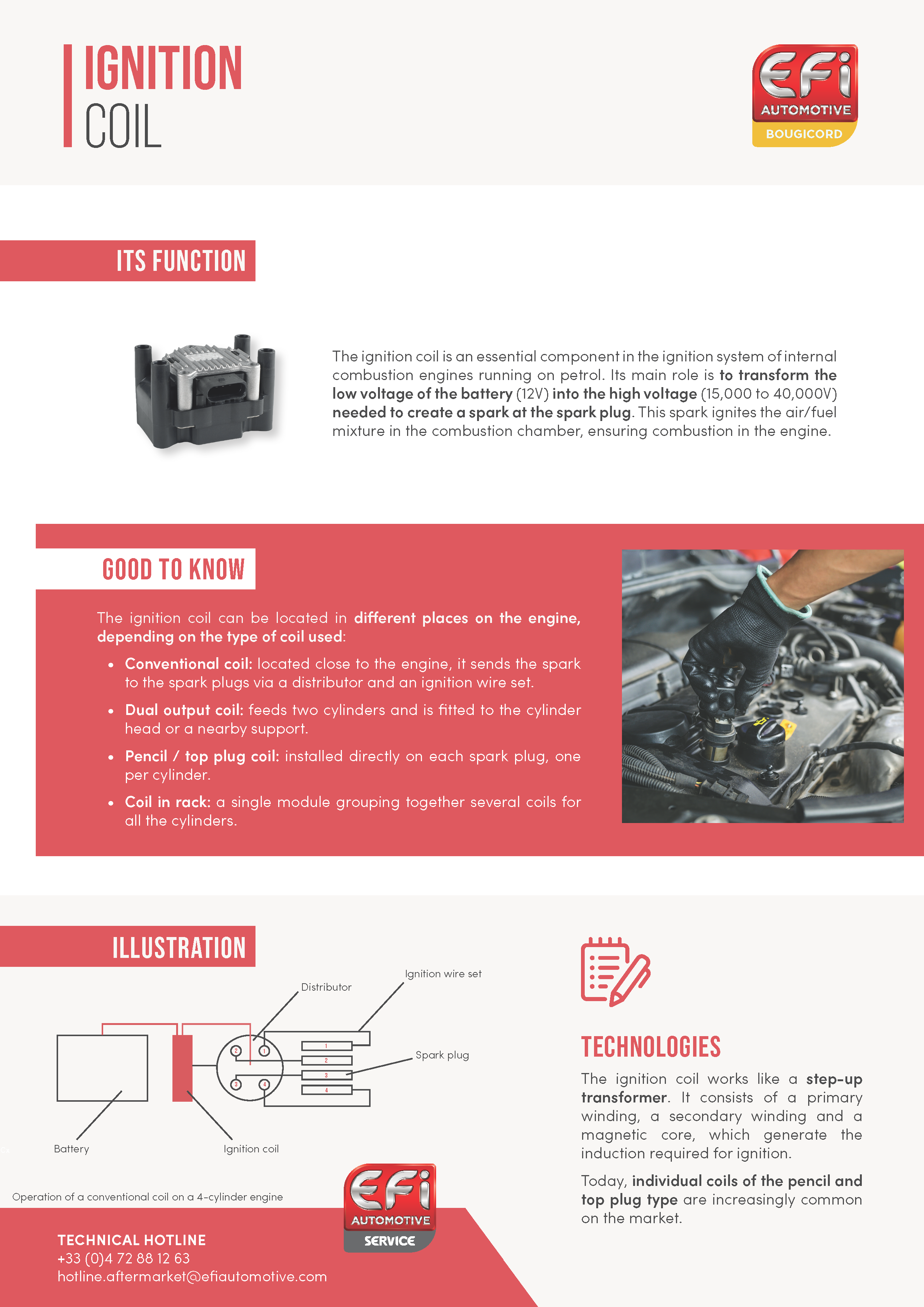
As a first step, we strongly recommend that you visually inspect the coil and its components, i.e. the wiring (presence of burnt, damaged, corroded or deteriorated wires), the ignition wire set (if it is a coil with a wire set) and the coil connector.
We also invite you to inspect the cap, the ignition wire or the coil housing to make sure that they are not burnt, damaged, cracked, corroded, deteriorated or that there is no water, oil or moisture present.
Secondly, using a multimeter, you can check that the coil is working properly by making sure that an electric current is present at the output of the connector.
In case of doubt, it is possible to swap the coils (in the case of pencil coils and/or top plug) in order to find the defective cylinder. However, we do not recommend changing only one coil.
If the previous tests are not conclusive, then it seems that you will have to replace the ignition coil(s) in your vehicle.